SSH - Secure Shell

SSH provides a mechanism for establishing a cryptographically secured connection between two parties, authenticating each side to the other, and passing commands and output back and forth. SSH using numbers of encryption techniques.
- Symmetric Encryption
- Asymmetric Encryption
- Hashes
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetrical encryption is a type of encryption where one key can be used to encrypt messages to the opposite party, and also to decrypt the messages received from the other participant. This means that anyone who holds the key can encrypt and decrypt messages to anyone else holding the key.
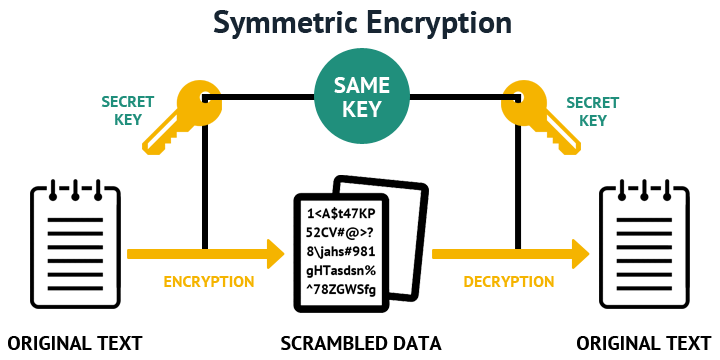
Symmetrical encryption is often called shared key or shared secret encryption
Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetrical encryption uses two separate keys for encryption and decryption. These two keys are known as the public key and the private key.
Asymmetrical encryption is different from symmetrical encryption in that to send data in a single direction
Hashes
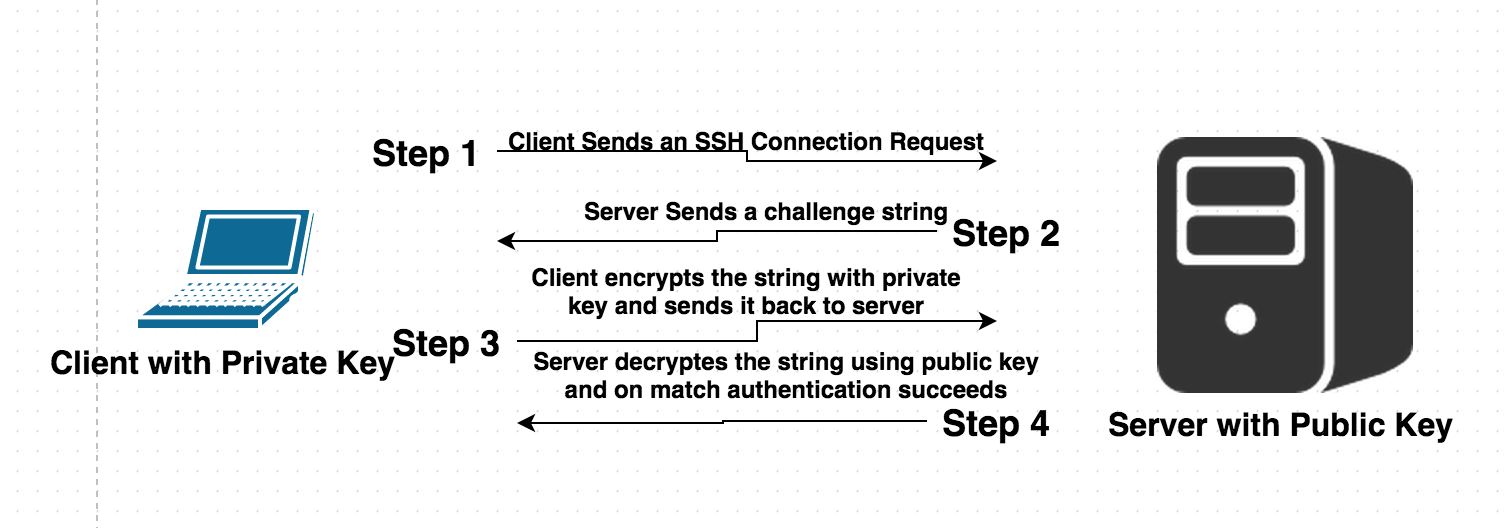
SSH (Secure Shell) public-key authentication relies on asymmetric cryptographic algorithms that generate a pair of separate keys (a key pair), one “private” and the other “public”.
Generate SSH KEY
1ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "your_email@example.com"
If you are using a legacy system that doesn't support the Ed25519 algorithm, use:
1ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"
When you're prompted to "Enter a file in which to save the key", you can press Enter to accept the default file location. Please note that if you created SSH keys previously, ssh-keygen may ask you to rewrite another key, in which case we recommend creating a custom-named SSH key. To do so, type the default file location and replace id_ALGORITHM with your custom key name.
1Enter file in which to save the key (/c/Users/YOU/.ssh/id_ALGORITHM):[Press enter]
At the prompt, type a secure passphrase
1Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): [Type a passphrase]
2Enter same passphrase again: [Type passphrase again]